| 1. |
______________ may be defined as the science of determining the position, in three dimensions, of natural and man-made features on or beneath the surface of the Earth. |
|
|
Monitoring |
|
|
Surveying |
|
|
Engineering |
|
|
None of the above |
| 2. |
What does DGM stand for? |
|
|
Digital grade model |
|
|
Digital ground model |
|
|
Digital geometric model |
|
|
None of the above |
| 3. |
Data abstraction, preliminary computations, data preparation and data entry are all areas where transcription errors are likely to lead to apparent blunders. Ideally all these activities should be carried out by more than one person so as to duplicate the work and with frequent cross-reference to detect errors. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 4. |
The ____________ is a technique of quality assurance. It is a means of guarding against a blunder or gross error and the principle must be applied at all stages of a survey. |
|
|
Safety control |
|
|
Independent check |
|
|
Cross check |
|
|
None of the above |
| 5. |
In the case of a control survey, the protection of survey monuments is most important since the precise coordinates of a point which no longer exists or cannot be found are useless. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
The simplest mathematically definable figure which fits the shape of the geoid best is an ______ formed by rotating an ellipse about its minor axis. |
|
|
Ellipsoid |
|
|
Secondary geoid |
|
|
Hypersoid |
|
|
Elliptical geoid |
| 7. |
The control points A,B,C..F in the following figure , coordinate positions of each point can be obtained by which of the following methods?
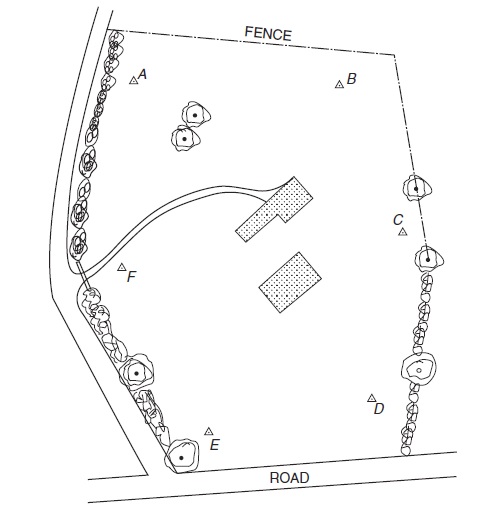
|
|
|
Intersection or resection |
|
|
Traversing |
|
|
Networks |
|
|
All the above |
| 8. |
A ______ survey needs to be precise, complete and reliable and it must be possible to show that these qualities have been achieved. |
|
|
Digital |
|
|
Aerial |
|
|
Control |
|
|
Principle |
| 9. |
A Digital Ground Model (DGM) is a ______________, mathematical representation of the landform and all its features, stored in a computer database. |
|
|
one-dimensional |
|
|
two-dimensional |
|
|
three-dimensional |
|
|
four-dimensional |
| 10. |
What does CAD stand for? |
|
|
Computer aided design |
|
|
Controls and design |
|
|
Controls and drafting |
|
|
Computers and design |
|